Search engines cannot visit your website endlessly. They give every site a limited amount of time and resources to crawl pages, understand them and update their index. This limit is often called crawl budget. In simple words, it is the number of pages Google can and wants to crawl on your website within a time period.
For business websites with many pages, this becomes very important. If Google does not reach your new pages or updated content in time, your important pages may not appear in search results quickly. This delay can affect visibility, traffic and even revenue. A slow crawl also means search engines might waste time on useless URLs instead of reaching the pages that help your business grow.
This guide gives you a clear and friendly checklist that business owners can follow without feeling lost. By the end, you will understand what to check, how to fix issues and how to make sure search engines spend more time crawling the pages that support your business goals.
Understand the Foundations of Crawl Budget
What is Crawl Budget
Crawl budget is a mix of two things. The first is crawl capacity, which is the number of pages Googlebot can fetch from your website based on your server’s health. If your server is slow or returns errors, crawl capacity goes down. The second is crawl demand, which depends on how important and fresh your content is. If your pages are useful and updated often, Google visits them more.
Both sides matter. A healthy and fast website encourages search engines to crawl more. At the same time, websites with helpful and updated content attract more crawl demand naturally. When these two come together, Google crawls your important pages faster and more often.
How Crawl Budget Affects Business Sites
If your website has hundreds or thousands of pages, poor control over crawl budget can harm your visibility. For example, imagine you launch a new product page or publish a new service page. If Google cannot reach it quickly, that page will not rank. This slows down your marketing and reduces the traffic you could have received.
Smaller business websites with fewer pages might not face serious crawl budget problems, but the practices shared in this guide still help keep the site clean organised and easier to crawl.
Pre Checklist – Audit Your Current State
Before you start fixing anything, check your current crawl situation. The first place to look is Google Search Console, inside the Crawl Stats report. It shows how often Google crawls your website, how many requests were made and how fast your server responded.
If you run a larger business website, you can also use log file analysis or a crawl simulation tool to understand which pages Google is visiting and which pages it is ignoring. This helps you identify hidden issues.
Once you have this data, set a baseline. Check how many pages Google crawls daily, how long it takes to respond and how many pages are discovered but still not indexed. This starting point helps you measure your improvements later.
Checklist – Optimize Crawl Budget Step by Step
1. Exclude Low Value Pages from Crawling

Search engines should spend their limited crawl time on your important pages. Low value pages such as login pages, print pages, admin sections or endless filter results should not be crawled. These pages usually do not help your customers and waste valuable crawl time.
You can block these pages using robots.txt, add noindex tags or use canonical tags if the content is similar to another page. Many CMS platforms auto create tag pages or archive pages that you might not need. Review them and decide whether they should be crawled at all.
2. Clean Up Duplicate Content and URL Parameter Issues
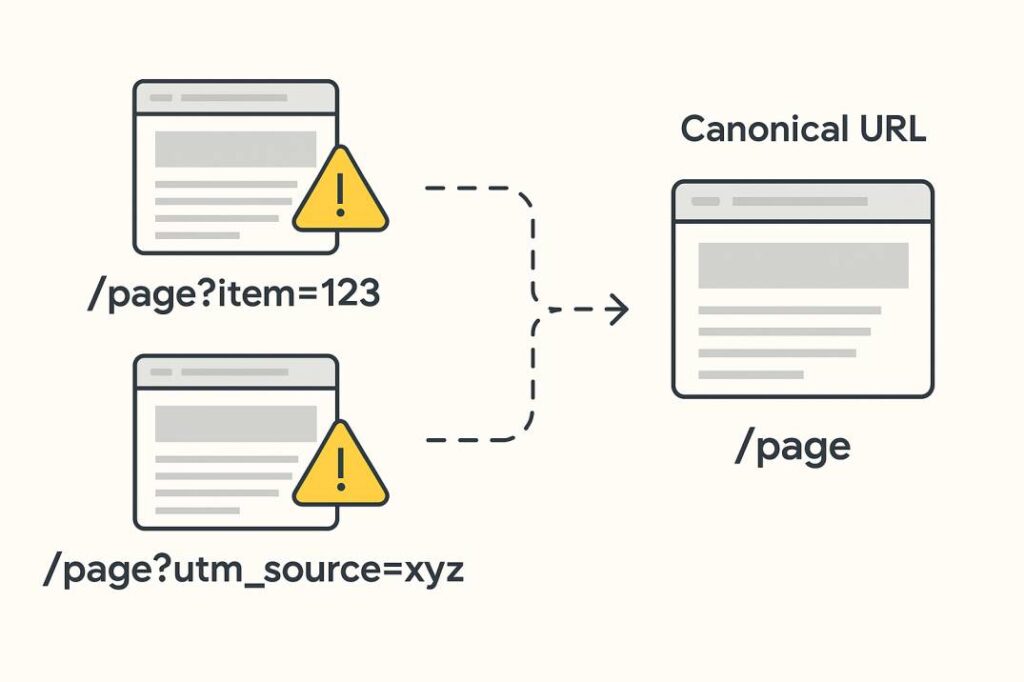
Duplicate content and messy URLs with tracking parameters can confuse Google. They also waste crawl budget because search engines crawl many versions of the same content.
Set up proper canonical URLs, fix redirect loops and make sure old URLs redirect correctly to the main version. Manage parameters in Google Search Console if your site generates multiple URL versions of the same content.
This simple work helps Google focus on the correct pages and reduces crawling waste.
3. Improve Site Speed and Response Time

Your crawl capacity increases when your website loads fast. Slow servers reduce how many pages Google can crawl in a session. Fast websites invite search engines to crawl more pages without causing server stress.
Business owners can take practical steps such as compressing images, enabling caching, reducing heavy scripts, using a CDN and choosing reliable hosting. If your site has many pages, make sure your hosting provider can support high crawl activity during busy times.
4. Ensure Proper Internal Linking and Sitemap Structure

Internal links tell search engines which pages matter. When you link to important product or service pages frequently, Google finds them faster. Strong internal linking also prevents orphan pages that have no links pointing to them.
Create an XML sitemap and submit it in Search Console. Large business websites can use multiple sitemaps for different sections such as blog, services or products. Always ensure new important pages are linked from your homepage or main sections so they get discovered quickly.
5. Mobile First and Crawl Friendly Version

Google crawls and indexes the mobile version of your website first. If your mobile site hides content, breaks navigation or does not link to important pages, your crawl demand will drop.
Check that your mobile navigation matches your desktop layout. Make sure product pages, service pages and internal links are visible on mobile. A clean and complete mobile version helps both users and search engines reach your best content easily.
6. Monitor and Fix Crawl Errors and Redirects

Problems such as redirect chains, soft 404s or server errors waste crawl budget. They also slow down your indexing process. Use tools like Screaming Frog to find long redirect chains and fix them. Check Index Coverage in Search Console to identify soft 404s or missing pages.
When you move or remove a page, make sure to set correct 301 redirects. Fixing these issues quickly helps Google spend more time on pages that bring value to your business.
7. Review Content Regularly and Remove Thin or Outdated Pages

Old or thin content can lower crawl demand. Search engines may decide these pages are not useful and they may stop crawling your site as often.
Audit your blog posts and service pages every few months. Update outdated content, merge similar pages or remove content that has no traffic or value. A clean and organised website encourages Google to crawl and index important pages more frequently.
Monitoring and Maintenance
Crawl budget optimization is an ongoing task. It is not something you fix once and forget. Keep an eye on Search Console reports to track crawl requests, response time and the ratio of discovered to indexed pages. These numbers show how healthy your site is.
If you manage a medium or large website, review log files monthly or run crawler tools to find new problems. Keep a simple note of updates or changes you make so you can compare crawl stats before and after.
Think of this as website maintenance that protects your long term visibility.
When to Prioritize Crawl Budget Optimization
Crawl budget matters most for large websites with more than ten thousand pages or for sites that publish new content frequently. If Search Console shows many URLs as discovered but not indexed, you should take crawl budget seriously.
Smaller business websites may not face serious shortages, but applying this checklist still keeps everything tidy and crawl friendly. Review your situation once a year and adjust based on your website growth.
Conclusion
Crawl budget optimization helps search engines focus on the most important pages of your website. When done correctly, your high value pages get indexed faster and appear in search results sooner. This helps your business reach customers and stay ahead of competitors.
Start by cleaning low value pages, fixing duplicate issues, improving speed, strengthening internal links, monitoring mobile performance and removing outdated content. Follow this checklist regularly to keep your website healthy and ready to scale.
Every business, small or large, can benefit from better crawl management. It is a simple step that brings long term results. If you want more guides like this, explore other SEO insights on SEO With Sachin and keep improving your online growth.
